By Raja Tabet, Sr. VP of Engineering, and Anand Thiruvengadam, Product Marketing Director, Custom Design and Physical Verification Group
Sponsored by Synopsys.
The adoption of 3DIC architectures is enjoying a surge in popularity as product developers look to their inherent advantages in performance, cost, and the ability to combine heterogeneous technologies and nodes into a single package. As designers struggle to find ways to scale with complexity and density limitations of traditional flat IC architectures, 3D integration offers an opportunity to continue functional diversity and performance improvements, while meeting form-factor constraints and cost.
3D structures offer a variety of specific benefits. For example, performance is often dominated by the time and power needed to access memory. With 3D integration, memory and logic can be integrated into a single 3D stack. This approach dramatically increases the width of memory busses through fine-pitch interconnects, while decreasing the propagation delay through the shorter interconnect line. Such connections can lead to memory access bandwidth of tens of Tbps for 3D designs, as compared with hundreds of Gbps bandwidth in leading 2D designs.
From a cost perspective, a large system with different parts has various sweet spots in terms of silicon implementation. Rather than having the entire chip at the most complex and/or expensive technology node, heterogeneous integration allows the use of the ‘right’ node for different parts of the system, e.g., advanced/expensive nodes for only the critical parts of the system and less expensive nodes for the less critical parts.
In this post, which was originally published on the “From Silicon to Software” blog, we’ll look at 3DIC’s ability to leverage designs from heterogenous nodes– and the opportunities and challenges of a single 3D design approach to achieve optimal Power, Performance, and Area (PPA).
Vertical Dimension Changes the Design Strategy
While 3D architectures elevate workflow efficiency and efficacy, 3DIC design does introduce new challenges. Because of the distinct physical characteristics of 3D design and stacking, traditional tools and methodologies are not sufficient to solve these limitations and require a more integrated approach. In addition, there is a need to look at the system in a much more holistic way, compared to a typical flat 2D design. Simply thinking about stacking 2D chips on top of each other is insufficient in dealing with the issues related to true 3D design and packaging.
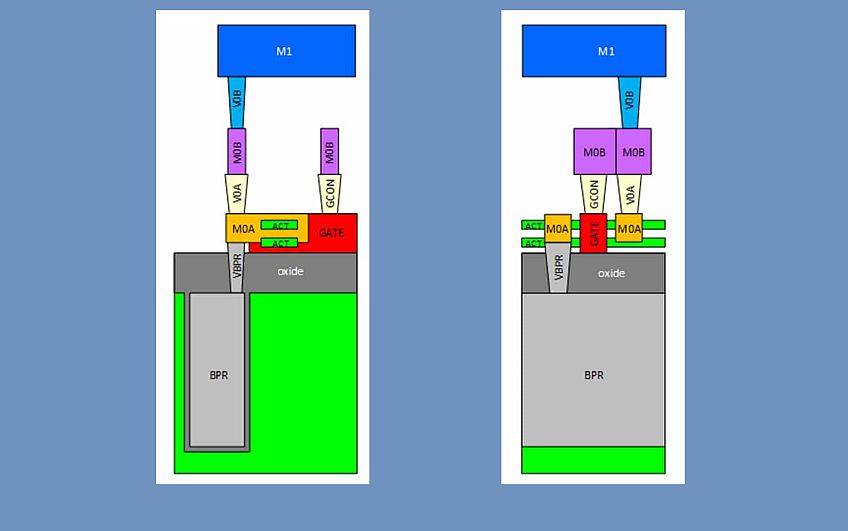
Since the designs must be considered in three dimensions, as opposed to the typical x, y aspects of a flat 2D design, everything must be managed with the addition of the z dimension – from architectural design to logic verification and route connection – including bumps and through-silicon vias (TSVs), thermal, and power delivery network (PDN) opportunities for new tradeoffs (such as interposer based versus 3D stacks, memory on logic or logic on memory, and hybrid bonding versus bumps). Optimization of the ‘holy grail’ of PPA is still a critical guiding factor; however, with 3DICs, it now becomes cubic millimeter optimization, because it’s not just in two directions, but also the vertical dimension that must be considered in all tradeoff decisions.
The need for Co-design Methodology
Further complicating matters, higher levels of integration available with 3DICs obsolete traditional board and package manual-level techniques such as bump layout and custom layout for high-speed interconnects, which cause additional bottlenecks. Most importantly, interdependency of previously distinct disciplines now needs to be considered in a co-design methodology (both people and tools), across all stages of chip design, package, architecture, implementation, and system analysis.
Let’s look at an example of a specific design challenge – the goal to improve memory bandwidth. Traditionally, designers would look at how to connect the memory and CPU to get the highest possible bandwidth. But with 3DICs, they need to look at both the memory and CPU together to figure out the optimal placement in the physical hierarchy, as well as how they connect, through CSVs or silicon vias, for example. While performance is critical, designers need a way to evaluate the power and thermal impact by stacking these types of elements together in different ways, introducing new levels of complexities and design options.
Taking a Silicon-First Approach
While it might seem obvious to consider a 3D architecture in a similar manner as a printed circuit board (PCB) design, 3DICs should ideally take a silicon-first approach – that is, optimize the design IP (of the entire silicon) and co-design this silicon system with the package. Within our approach to 3DICs, Synopsys is bringing key concepts and innovations of IC design into the 3DIC space. This includes looking at aspects of 3DICs such as architectural design, bringing high levels of automation to manual tasks, scaling the solution to embrace the high levels of integration from advanced packaging, and integrating signoff analysis into the design flow.
3DICs integrate the package, traditionally managed by PCB-like tools, with the chip. PCB tools are not wired to deal with both the scale complexity and process complexity. In a typical PCB there may be 10,000 connections. But in a complex 3DIC, there are hundreds of millions of connections, introducing a whole new level of scale which is far outpacing what older, PCB-centric approaches can manage. Existing PCB tools cannot offer assistance for stacking dies, and there is no package or PCB involved. Further, PCB tools cannot look at RTL or system design decisions.
The reality is that there cannot be one single design tool for all aspects of a 3DIC (IC, interposer, package), yet there is an acute need for assembling and visualizing the complete stack. The Synopsys 3DIC Compiler does just that. It is a platform that has been built for 3DIC system integration and optimization. The solution focuses on multi-chip systems, such as chip-on-silicon interposer (2.5D), chip-on-wafer, wafer-on-wafer, chip-on-chip, and 3D SoC.
The PPA Trifecta
Typically, when you think of large complex chips, the first optimization considered is area. SoC designers want to integrate as much functionality into the chip and deliver as high performance as possible. But then there are always the required power and thermal envelopes, particularly critical in applications such as mobile and IoT (and also high-performance computing). Implementing 3D structures enables designers to continue to add functionality to the product, without exceeding the area constraints and, at the same time, lowering silicon costs.
But a point tool approach only addresses sub-sections of the complex challenges in designing 3DICs. This creates large design feedback loops that don’t allow for convergence to an optimal solution for the best PPA per cubic mm2 in a timely manner. In a multi-die environment, the full system must be analyzed and optimized together. It isn’t enough to perform power and thermal analysis of the individual die in isolation. A more effective and efficient solution would be a unified platform that integrates system-level signal, power, and thermal analysis into a single, tightly coupled solution.
This is where 3DIC Compiler really shines–by enabling early analysis with a suite of integrated capabilities for power and thermal analysis. The solution reduces the number of iterations through its full set of automated features while providing power integrity, thermal, and noise-aware optimization. This helps designers to better understand the performance of the system and facilitate exploration around the system architecture. And it also allows a more efficient way to understand how to stitch together various elements of the design and even connect design engineers in some ways to traditional 2D design techniques.
Ideal Platform for Achieving Optimal PPA Per Cubic mm2
Through the vertical stacking of silicon wafers into a single packaged device, 3DICs are proving their potential as a means to deliver the performance, power, and footprint required to continue to scale Moore’s law. Despite the new nuances of designing 3D architectures using an integrated design platform, the possibilities of achieving the highest performance at the lowest achievable power makes 3D architecture appealing. 3DICs are poised to become even more widespread as chip designers strive to achieve the optimum PPA per cubic mm2.